Economic and strategic analysis of scientific journals:
recent evolutions
recent evolutions
INTRODUCTION
As a consequence of the use of modern information technology, a lot of changes are going on in academic publishing. Many scholarly journals are available online and there are also a large number of e-only journals, often published outside the range of traditional publishers. There is also a worldwide movement advocating open access for scientific information. It is an interesting issue how these developments have influenced the policy of traditional publishers.
This article is mainly about commercial publishers. It analyses a number of aspects of the behaviour of these publishers, also taking into account the changes in the system. Section 2 deals with the publishers' pricing policy. Many libraries suffer from the so-called serials crisis caused by the huge price increases for scholarly journals. What causes these price increases and are they justified? Section 3 goes into the market of scholarly publishing: is it really operating as a commercial market? Is there enough competition and how does the large number of acquisitions influence this? Section 4 is about licensing. The traditional library subscription model is being replaced by site licenses for the electronic full text. We are confronted with the so-called Big Deals, which are highly controversial among librarians. Section 5 is about 'Open access': what does it mean and how do commercial publishers react to the open access movement. The article ends with some concluding remarks about possible scenarios for the academic community.
PRICING POLICY
There has been a lot of discussion about the so-called serials crisis: price increases of scholarly journals causing cancellations
by libraries, which in turn are followed by new price increases. This is illustrated by the following graph (Case, 2001).
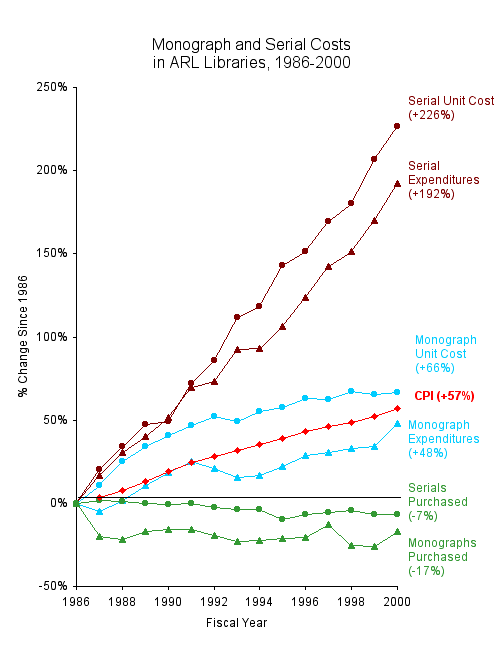
Graph 1: Monograph and Serial Costs in ARL libraries 1986 - 2000 (Case, 2001).
What are the causes for the increasing prices of scholarly journals? Are these price increases justified at all?
First, let us take a look at the cost of publishing.
According to King and Tenopir (1998) the average total costs of an article are $ 6.000, including the costs of the preparation of the manuscript, which takes the average author 80 to 100 hours. The publisher does of course, not meet the costs of the preparation by the author. The average article is read 900 times. It follows that the cost per reading, including author's preparation costs, are $ 6,70.
Let us take a closer look now at the publisher's costs.
King & Tenopir (1998) calculate that the fixed costs of the publishing process for an average journal are $ 400.000. Fixed costs are the costs for processing (such as receiving, reviewing, editing, proofing, typesetting of an article and of non-article pages) and support (such as administration, space and utilities, and taxes). They are called fixed costs because the cost parameters and elements should not vary with the number of subscriptions. The incremental costs per subscription (the costs for reproduction and distribution) are $ 40 per subscription.
Now we can calculate what subscription price a publisher needs for cost recovery:
| • | for a journal with 500 subscriptions $ 847 |
| • | for a journal with 5000 subscriptions $ 120 |
Since the average number of journal subscriptions is 1900, the average price to meet the publisher's costs is $ 252.
Now, let us look at some examples of journal prices and their increase between 1995 and 2001.
Table 1. Sample of journal prices (Case, 2001)
| 1995 | 2001 | %Change | |
| Brain Research | $10,181 | $17,444 | 71.3% |
| Biochem. Biophys. Acta | $ 7,555 | $12,127 | 60.5% |
| Chem. Phys. Letters | $ 5,279 | $ 9,637 | 2.6% |
| Tetrahedron Letters | $ 5,119 | $ 9,036 | 76.5% |
| Eur. Jrnl. of Pharmacology | $ 4,576 | $ 7,889 | 72.4% |
| Gene | $ 3,924 | $ 7,443 | 9.7% |
| Inorganica Chem. Acta | $ 3,611 | $ 6,726 | 6.3% |
| Intl. Jrnl. of Pharmaceutics | $ 3,006 | $ 5,965 | 98.4% |
| Neuroscience | $ 3,487 | $ 6,270 | 79.8% |
| Theoretical Computer Science | $ 2,774 | $ 4,608 | 6.1% |
| Jrnl. of Exp. Marine Bio. & Eco. | $ 1,947 | $ 3,501 | 79.8% |
It is an interesting question whether these price increases differ by type of publisher. Are they the same for commercial publishers and non-profit publishers? From the following overview, it can be seen that there are large differences between the different types of publishers and that commercial publishers have the largest increase.
Table 2. Average price increase by type of publisher (Tenopir & King, 2000)
| Average price | increase factor | |||
| 1975 | 1995 | current $ | constant $ | |
| commercial | $ 55 | $ 487 | 8,9 | 3,1 |
| society | $ 28 | $ 229 | 8,2 | 2,9 |
| educational | $ 15 | $ 81 | 5,4 | 1,9 |
| other | $ 40 | $ 119 | 3,0 | 1,1 |
| all types | $ 39 | $ 284 | 7,3 | 2,6 |
There are also differences between the disciplines, as can be seen from the following table which shows the price per page and the price per citation for several disciplines. It distinguishes between profit and non-profit publishers. In all cases the profit publishers calculate higher prices than the non-profit publishers.
Table 3. Cost effectiveness comparisons (Bergstrom & Bergstrom, 2001a)
| price/page in $ | price/citation in $ | |||
| Field | for-pr | non-pr | for-pr | non-pr |
| Ecology | 1.19 | 0.19 | 0.73 | 0.05 |
| Economics | 0.81 | 0.16 | 2.33 | 0.15 |
| Atmos. Science | 0.95 | 0.15 | 0.88 | 0.07 |
| Mathematics | 0.70 | 0.27 | 1.32 | 0.28 |
| Neuroscience | 0.89 | 0.10 | 0.23 | 0.04 |
| Physics | 0.63 | 0.19 | 0.38 | 0.05 |
In addition to this, the next table shows cost effectiveness comparisons from a study from 1988. It presents cost/impact ratios for some disciplines. Lower cost/impact ratios mean greater cost effectiveness. Again, there is a striking difference between profit and non-profit publishers.
Table 4. Cost effectiveness comparisons: Cost/impact ratio (Barschall,1988)
| Profit | Non-profit | |
| Physics | 14.61 | 8.23 |
| Economics | 42.62 | 11.55 |
| Neuroscience | 8.69 | 0.64 |
Notwithstanding their high subscription fees, the profit publishers have a large share of the market. The following table illustrates this for the STM market (Science, Technology and Medicine). It presents for the largest publishers their number of journals (in 1998) and their share (as a percentage) of the total number of journals. It can be seen that 15 publishers constitute 50% of the market. The eight largest publishers are commercial.
Table 5. Publishers of ISI-rated STM journals (OFT, 2002)
| 1998 number | share % | ||
| 1.Elsevier Science | Commercial | 1347 | 18 |
| 2.Wolters Kluwer | Commercial | 552 | 7 |
| 3.Blackwell | Commercial | 341 | 4 |
| 4.Bertelsmann | Commercial | 326 | 4 |
| 5.Wiley | Commercial | 279 | 4 |
| 6.Taylor & Francis | Commercial | 191 | 2 |
| 7.Sage | Commercial | 123 | 2 |
| 8.Karger | Commercial | 101 | 1 |
| 9.Inst. E&E Engineers | Society | 93 | 1 |
| 10 Cambridge Un. Press | univ. Press | 84 | 1 |
| 11 Gordon & Breach | Commercial | 84 | 1 |
| 12 Oxford Un. Press | univ. Press | 83 | 1 |
| 13 Marcel Dekker | Commercial | 76 | 1 |
| 14 Holzbrinck | Commercial | 67 | 1 |
| 15 Am. Inst. Of Physics | Society | 41 | 1 |
| Others (2034 publishers) | 3922 | 50 |
What are the reasons for these price increases in commercial scientific publishing? (Office of Fair Trading, 2002, McCabe 1998).
Does the price inflation reflect increased costs? An extensive review of the relevant literature revealed that the actual cost of journal editing and printing do not seem to have suffered any unusual run-up during the past decade.
Reed Elsevier often presents the argument that there has been investment in the development of electronic methods for delivering journals by email and over the Internet, and that the number of articles published in each journal has increased significantly. But at the same time, one might expect that the increasing use of information technology should reduce the marginal costs associated with producing and delivering journals. Furthermore, while the same developments can be observed with non-profit publishers, the average prices of commercial journals, nevertheless, appear to be substantially higher than those of non-profit journals.
Are the price increases the consequence of a simple application of supply and demand analysis? Library budgets are rather fixed so large increases in the population of available titles might induce librarians to cancel some titles as they add new ones. A decline in a title's circulation will eventually force firms to raise prices as they attempt to cover the fixed costs of publication. In other words, everything else equal, a smaller subscriber base necessitates higher prices. Demand for new titles eventually results in higher prices across the board. But analysis by Roger Noll (referred to by McCabe, 1999) shows that significant price inflation has occurred independent of changes in circulation. That is, even after accounting for the effect of circulation on prices, there remains a large unexplained increase in prices.
Do these price differences perhaps reflect differences in circulation size and discipline? Surveys covering a wide variety of academic disciplines report that the prices of many commercial journals appear much higher that non-profit alternatives, even when allowing for some key sources of difference. As can be seen from Table 3, for-profit journals were almost five and a half times more expensive than non-profit journals in terms of price per page, and over ten times more expensive in terms of price per citation.
Another explanation might be that commercial publishers produce a high proportion of journals with small print runs. In an industry with high fixed costs and low variable costs per journal, this could result in higher average costs for commercial publishers. There is, however, no evidence for this.
If commercial publishers use their more profitable journals to support less profitable ones, this might explain the high prices for the former. However, it is far from clear why commercial publishers would want to do that. It also would not help to explain the overall observed price disparity.
An alternative hypothesis might be that the publishers offer subsidised subscriptions to individuals, and this contributes to price increases for institutions ('cross subsidisation'). However, there is no evidence that this is the case.
Furthermore, there is no evidence on the failure rate of new titles, which might indicate high risk as a justification for high prices. In addition to this, Wyly (1998) has analysed that the overall profitability of commercial STM publishing is high, not only in comparison to non-profit journals, but also in comparison to other commercial journal publishing.
Usually competition brings forward a decrease of prices; are there any factors that might prevent competition from working in scientific publishing? This is the topic of the next section.
COMPETITION AND MERGERS
There are a number of aspects that are typical for the market of scholarly journals, especially in the STM sector. First, there is inelastic demand: price competition is not a dominant feature of the market. Many journals have a particular reputation and there is often unwillingness of researchers and institutions to substitute a cheaper journal for an expensive one. The price sensitivity of demand for many journals is thus very low and journals are generally perceived as competing on quality rather than price. Certain journals can even be regarded as markets in their own right. Secondly, there are certainly barriers to entry ('positional advantage'): it appears to be very difficult for a new journal to become established and secure a strong reputation. Also, on the demand side, the limited budget of libraries is an immediate barrier to establishing a new journal successfully. On the supply side, the overall position of the leading journals remains very strong in almost all fields of STM research.
Is there any reason to expect that competition might work better from now on?
Price increases of, for instance Elsevier Science, used to be more than 10% per year but are recently not as large as they used to be:
| 2000 | 7,5% |
| 2001 | 6,7% |
| 2002 | 6,5% |
We have to keep in mind, however, that the US Consumer Price Index (CPI) in these 3 years together was only 8%. There also is not much influence to be expected from 'buyer power': historically buyer power does not appear to have constrained price increases by commercial scientific journal publishers.
Considerations as described above have led the Office of Fair Trading to the following conclusion: "We believe that there is evidence that the market for STM journals may not be working well." (Office of Fair Trading, 2002)
In this context, a striking phenomenon in the commercial scientific publishing market is the number of mergers and acquisitions. Mergers and acquisitions result, of course, in a small number of rather large market players.
Robinson (2003) gives an overview of mergers and acquisitions in the period 1990-2000:
| • | Bertelsmann buys Random House for $ 1.5 billion; |
| • | Bertelsmannn buys 80% of Springer Verlag for $ 600 million; |
| • | Elsevier buys Compendex; |
| • | Wolters Kluwer buys Plenum; |
| • | Pearson buys Simon & Schuster for $ 4.6 billion; |
| • | AOL buys Time Warner for $ 165 billion; |
| • | CSA buys R.R. Bowker; |
| • | Taylor & Francis buys Gordon & Breach for $ 31.5 million; |
| • | Vivendi buys Houghton Mifflin for $ 2.2 billion; |
| • | Reed Elsevier buys Harcourt General for $ 5.7 billion; |
| • | Wolters Kluwer buys Ovid Technologies for $ 200 million; |
| • | Wolters Kluwer buys SilverPlatter; |
| • | Swets and Blackwell merged in 2000 and acquired Martinus Nijhoff; |
| • | Elsevier buys Endeavour. |
And very recently Cinven & Candover made their intention to purchase Bertellsmann Springer (with Kluwer Academic) known; this would result in the second largest publisher in the world.
From the library world there is often a lot of opposition towards mergers and acquisitions. They turn, for instance, to the Office of Fare Trading in the UK and to the regulatory authority in the US, the Federal Trade Commission and Department of Justice. In the US, the antitrust rule of thumb is that a merger or purchase must give one firm control of at least 35 % of the marker to trigger an intervention.
But competition among STM journals does not function in the same manner as it does among trade magazines because each journal is a unique entity with a reputation and position in the scientific world and some core titles are indispensable to coverage of a field. Mark McCabe (1999, 2001) has analysed the STM market and notes that the 35% market share rule for customarily market monopoly control does not apply. Because each journal has a narrowly defined focus, one title cannot be substituted for another. He proposed a portfolio model that identifies a core group of titles and traced their prices as a group, by publisher, enabling him to identify increases due to merger effects. All else equal, publishers set prices so that higher use (or quality) journals exhibit lower cost-per-use ratios. Thus, most libraries purchase higher use journals. Conversely, fewer, relatively high budget libraries purchase lower use journals. Higher use imparts a cost advantage that makes it more profitable for their publishers to price low and sell widely. Using this model it is possible to show, in some cases, that mergers are profitable for journal publishers. A corollary is that the merged firm's journal prices increase. The merged firm is able to internalise certain pricing externalities that the merging parties fail to consider when they act independently. Larger portfolio firms are better able to capture these benefits and therefore, all else equal, set prices at a higher level. McCabe's conclusion is that mergers increase subscription costs. The following examples support this conclusion. After Elsevier (190 biomedical titles) bought Pergamon (57 biomedical titles), Pergamon titles increased 27% and Elsevier prices increased 7%. The Lippincott/Kluwer merger generated a postmerger (1991-1994) price increase of 35% in former Lippincott titles. Thus, economies of scale, if achieved, were not passed on to the subscribers.
In addition to this, societies' journals are taken over by commercial publishers:
| • | 10 of Elsevier's 13 new titles in 2001 were drawn from scholarly associations. |
| • | 10 of Sage's 35 new titles in 2002 represented societies' contracts. |
How do the customers of these publishers, the libraries, respond to these developments?
As we have seen from Graph 1, there is a decrease in the number of books purchased, as a larger percentage of the budget is spent on journals. But there is also a decrease in the number of subscriptions, as a result of often painful journal cancellation projects. Cancellation of subscriptions has resulted in improved document delivery and interlibrary loan services in a lot of countries or even cross-national. And, finally, libraries have formed consortia for purchasing journals at discounted prices. Thus far, successes in this field have been reached in Canada (CNSLP) and the UK (NESLI) (Robinson, 2003). There are also a number of initiatives in the field of e-publishing that put some pressure on commercial publishers. For this, I refer to section 5 about Open Access.
LICENSING
Almost 75% of the current academic journals have gone online, even as they continue to be published in print. This led especially the larger commercial publishers to introduce the so-called Big Deal: an online aggregation of journals that publishers offer as a one-price, one size fits all package (Frazier, 2001). It is all or nothing: if it is possible at all to get a license for an individual part, this part of the bundle is even more expensive than the whole bundle. The price of these arrangements, thus far, is motivated by historical facts, mostly the amount the institution used to pay for the print subscriptions in the years before. Sometimes a fee is added for the electronic access, sometimes with a reduction if you cancel the print. The price increases per year, and the increase is always more than the current price index (CPI). Thus, we are not only confronted with large publishers, but also with large bundles.
To illustrate the success of these deals, here are some figures for Elsevier Science.
Table 6. Market penetration of Science Direct (Scholarly Communications Report, 2002)
| 2000 | 35% |
| 2001 | 69% |
| 2002 | 75% |
It is difficult, if not impossible, to compare the license conditions for different institutions or countries because most of the agreements contain non-disclosure or confidentiality clauses: you are not entitled to share the information in the agreement with a third party.
A spokesman of Elsevier Science explained this as follows: "It would generate more confusion and possibly consternation among customers who might not understand why there could be a discrepancy."
This phenomenon of Big Deals has a number of negative consequences.
| • | Control mechanisms on demand and supply side disappear. It is all or nothing, regardless of whether you want the whole or only a part. |
| • | There is no possibility to cancel individual titles. Subscribing to a part of the bundle is more expensive than a license for the whole. |
| • | The chance of effective entry of new titles is low. Most library budgets are fixed or decreasing. The spending of a library budget is fixed for several years by these Big Deals and the prices increase without a possibility to cancel individual titles. Consequently, there is no possibility to free a part of the budget for new journals. |
| • | The exit of the smallest publishers is more than likely. Large parts of library budgets are spend on the Big Deals. Libraries in most cases cannot afford to cancel the Big Deal licenses. Thus, in case of budgetary problems, subscriptions for journals outside the Big Deals are likely to be cancelled. |
| • | Increasing problems as a result of mergers: larger publishers offer larger bundles; consequently, the negative effects of mergers described above occur to a larger extent. |
It is often argued that these Big Deals may have some negative effects, but they really are for the benefit of the academic community. However, research by Bergstrom & Bergstrom (2001b) has shown that journal site licenses are for the benefit of the academic community only if the subscription price is close to the publisher's average cost. If this is not the case, the selling of individual subscriptions would result in greater net benefits for the academic community. This applies to the site licenses offered by commercial publishers. If these publishers would be confronted with this in negotiations, they would have two options: drop the price significantly, or negotiate with individuals or at least a large number of institutions within each university.
One might think that site licenses might solve the problem of interlibrary loan (ILL). The volume of ILL in 2000 in the US is estimated to be 40 million copies (Tenopir & King, 2000). It is, as we have seen, the result of the cancellations of journal subscriptions due to price rises. This system, however, is highly inefficient because a lot of costs are involved in the copying of journal articles. In the site licenses, electronic ILL is not permitted. So if you have a site license and another institution requests a copy of a journal article, you have to print it first and then copy or scan it for delivery. This is ridiculous. An alternative could be a pay-per-view system offered by the publishers. But at this moment pay-per-view in Science Direct, for instance, costs $ 30 per article. Here we have a remarkable situation. The ILL systems do not generate any income for publishers. It is rather easy to think of a new system that could benefit publishers, libraries and end-users. For instance, if electronic ILL were permitted to libraries and they would pay the publishers some fee for every transaction then:
| • | publishers would earn additional money, |
| • | libraries would get rid of a highly inefficient service, |
| • | end-users would get their information online and quicker than in the traditional system, while the price could probably be lowered. |
Another solution would be that publishers introduce a pay-per-view system for a price that is comparable to the present ILL prices. Publishers, however, are afraid of loss of turn over. Their nightmare probably is that all subscriptions are cancelled and that everybody will switch to ILL or pay-per-view. Differentiating for different kinds of institutions might prevent this, but thus far the larger commercial publishers take no initiative. So the present, highly inefficient situation continues.
OPEN ACCESS
There is a worldwide movement to promote open access to scientific information. The Public Library of Science (PloS), SPARC and the Budapest Open Access Initiative are examples of this.
To prevent misunderstanding: 'open access' does not mean that there are no costs involved. Of course there are costs involved in publishing activities. 'Open access' means that the costs are not paid by the reader.
Who is paying in open access models? There are several possibilities (Savenije, 2002).
| • | The authors may pay for publication, as a kind of page charge. The Florida Entomological Society, for instance, lets authors pay when they want (in addition to a print article) immediate free web access (a so-called IFWA fee). Authors do profit from this online access because it is shown that the number of citations rises by providing web access. |
| • | Authors, or the institutions that employ them, may pay for the peer review because they profit from the acceptance of their contribution (for instance The Review of Economic Theory). |
| • | Institutions or societies may support a journal or site when they need a medium for their own discipline. This, for instance, is the case with the International Journal of Integrated Care (IJIC), published with the support of Igitur, Utrecht Publishing & Archiving Services. The start of this journal was supported by a number of research groups working in this field.. |
| • | Institutions or societies may buy the right for their members to publish in a certain journal or on a site. This is the case with BioMed Central, a profit organisation introducing new financial models for academic e-publishing. |
| • | Finally, of course, there is the possibility of grants, donations, or sponsorships, by (inter)national funding agencies, organisations like SPARC, or others. |
A large number of publishing activities with open access have been undertaken. There is a Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ) maintained by the University of Lund. In addition to this, a large number of university libraries are working on so-called institutional repositories. The library collects the e-version of every document that is published within its university, stores these publications, and offers free access through the university's website. This, of course, can be combined with institutional and personal homepages. If, in the long run, all publications are thus collected, these can be made accessible by discipline-oriented portals.
If an article is published in a journal, you need the permission of the publisher to put an e reprint on the website of the university. Some publishers give this permission, some do not. Larger commercial publishers are reluctant to give permission. They are afraid that subscriptions will be cancelled. There is also the possibility of free web access (immediately or later) by the publishers themselves. That is in line with the policy of the Public Library of Science, which in 2001 demanded that every article should get free web access six months after publication. Up to now, only a small number of smaller commercial publishers offer free web access after a period of time. In fact, it is clear and not very surprising that large commercial publishers consider the open access movement to be a threat. Whatever may come out of this movement, it puts some pressure on the publishers to change their policy because in the long run they may not be indispensable.
CONCLUDING REMARKS
Electronic publishing opens up new possibilities for scientific communication. Librarians see the possibility of open access as the main advantage of e-publishing. It is quite obvious that commercial publishers also favour e-publishing, but mainly as a means towards higher profits. In the long run, the changes in scientific communication may become a threat for traditional publishers. In the short run, a number of trends can be observed in commercial publishing.
| • | Benefits of scale will increasingly accrue to larger publishers. |
| • | Margins are likely to expand for those publishers with successful online platforms. The profitability improves by 15% as they move from print + online to online only. |
| • | Budget cuts for libraries are more than likely in the years to come and they will cause a cyclical slowdown in the publishing industry. |
So, what is there to do for the academic community confronted with the commercial publisher's policy directed towards higher profits? The following scenarios are possible.
| • | Influence the market by collective bargaining. In some countries there is already a policy of collective bargaining. But one could also imagine a situation in which consortia in several countries co-operate to get the same licensing conditions. This may be more difficult if agreements are made for a number of years because this makes it more difficult to synchronise negotiations. This may be an argument in favour of agreements for a shorter term, for instance, one year. |
| • | A smaller role for traditional impact factors. Scientists are to a high degree dependent on the quality judgement system that goes together with journal publishing and which is based on the impact factors of journals. If the role of the system would be diminished, it would become easier for authors to publish in other, for instance open access, journals. |
| • | Change intellectual property rights. If authors would not have to transfer their rights to the publisher, their articles could be published simultaneously on the university's website. The academic community, then, would no longer be dependent on commercial publishers for the distribution of the information. This could eventually result in a situation in which the publisher would still be responsible for the organisation of the quality judgement, but not really for the distribution anymore. |
| • | Decoupling the reporting and dissemination of research from commercial publishing. The dissemination of the results, then, could go through the institution's website. Of course, publishers still could provide services for quality assessment. |
The present commercial system of scholarly publishing certainly has a number of disadvantages. It is apparent that one can think of models of scientific communication that are more in tune with the demands of the academic community. However, it is far from clear how the transition from the present model to another model could take place. Commercial publishers are very reluctant to innovate the system. Therefore, the academic community should take its responsibility and start initiatives for innovation itself.
REFERENCES
Barschall, Henry H. (1988). "The Cost-Effectiveness of Physics Journals." Physics Today, 41 (17).
Bergstrom, Carl T. & Theodore C. Bergstrom (2001a). "The Economics of Scholarly Journal Publishing." http://octavia.zoology.washington.edu/publishing/
Bergstrom, Carl T. & Theodore C. Bergstrom (2001b). "Do Electronic Site Licenses for Academic Journals Benefit the Scientific
Community?" http://ideas.repec.org/p/fth/calaec/15-01.html
Case, Mary M. (2001). "Scholarly Communication. A system in crisis." Pittsburgh Conference 2001.
Frazier, Ken (2001). "The Librarian's Dilemma. Contemplating the Costs of the 'Big Deal'". D-Lib Magazine, 7 (3). http://www.dlib.org/dlib/march01/frazier/03frazier.html
King, Donald W. & Carol Tenopir (1998). "Economic Cost Models of Scientific Journals." Paper presented to the ICSU Press Workshop,
Keble College, Oxford, UK, 31 March to 2 April 1998. http://www.bodley.ox.ac.uk/icsu/kingppr.htm
McCabe, Mark (1998). "The impact of publisher mergers on journal prices: a preliminary report." ARL, issue.200, October 1998. http://www.arl.org/newsltr/200/mccabe.html
McCabe, Mark (1999). "The impact of publisher mergers on journal prices: An Update." ARL, issue 207, December 1999. http://www.arl.org/newsltr/207/jrnlprices.html
McCabe, Mark (2001). "The Impact of Publisher Mergers on Journal Prices: Theory and Evidence." The Serials Librarian 40, pp. 157-166.
Office of Fair Trading (2002). The Market for Scientific, Technical and Medical Journals. September 2002. http://www.oft.gov.uk/nr/rdonlyres/......../oft396.pdf
Robinson, Kathleen (2003). "Mergers, Acquisitions, and Access: STM Publishing Today." Library and Information Systems in Astronomy IV. US Naval Oberservatory, Vol. XXX.
Savenije, Bas (2002). "Who pays the Ferryman? About new models for scientific communication." Paper presented at the international
symposium "Science & Engineering Libraries for the 21st Century". Leuven, Belgium, October 2-4, 2002. http://www.library.uu.nl/staff/savenije/publicaties/leuventekst.htm
Tenopir, Carol & Donald W. King (2000). "Towards Electronic Journals." SLA Publishing, Special Libraries Association.
Tenopir, Carol & Donald W. King (2001). "Lessons for the future of journals." Nature, 18 October 2001. http://www.nature.com/nature/debates/e-access/Articles/tenopir.html
Wyly, Brendan J. (1998). "Competition in Scholarly Publishing? What Publisher Profits Reveal." ARL, issue200, October 1998. http://www.arl.org/newsltr/200/wyly.html
WEB SITES REFERRED TO IN THE TEXT
BioMed Central. http://www.biomedcentral.com/
Budapest Open Access Initiative (BOAI). http://www.soros.org/openaccess/index.shtml
Directory of Open Access Journals. http://www.doaj.org/.
Igitur, Utrecht Publishing & Archiving Services. http://www.igitur.uu.nl/en/default.htm
International Journal of Integrated Care. http://www.ijic.org/
Public Library of Science (PloS). http://www.publiclibraryofscience.org/
The Review of Economic Theory. http://www.elsss.org.uk/?current=Review+of+Economic+Theory).
SPARC - The Scholarly Publishing and Academic Resources Coalition. http://www.arl.org/sparc/
LIBER Quarterly, Volume 13 (2003), No. 3/4